Enterprise Capabilities
Enterprise Capabilities
So, what are capabilities, exactly? A capability is an abstraction that represents the ability to perform a particular skillset. In organizations, these would be considered organizational capabilities, directional capabilities, service capabilities, information capabilities and technology capabilities. During this research webinar, we will take a closer look at different types of capabilities, and explain how they work in practice.
We will also be taking a closer look at whom (organizational role or actor) or what (impersonal role, i.e. applications/systems) actually delivers the output of an executed capability, and through which context is the capability processed and delivered. Moreover, there also needs to be a connection between different capabilities and a clear identification of, perhaps most importantly, who is the actual targeted beneficiary of the capability output (value proposition and consumers).
Research Focus
Information and research is sought on topics related to the understanding and comparison of Enterprise Capability concepts, including, but not limited to:
- What are Capabilities and what are Enterprise Capabilities?
- What does Enterprise Capabilities include?
- Which different Enterprise Capabilities concepts exist
- What are the most common Enterprise Capabilities concepts, method and approaches applied
- Compare various Enterprise Capabilities concepts, method and approaches
- Ontology foundations of Enterprise Capabilities concepts
- What common Enterprise Capabilities class type objects exist?
- Which common Enterprise Capabilities stereotype and subtype objects exist?
- What are the most common object descriptions?
- How do these class, stereo, type and sub-type objects semantically relate
- Is there a pattern in the objects and relationships, where a generic conceptual structure could be derived?
- Can an Enterprise Capabilities meta model be created
- Capability Modeling and viewpoint considerations:
- Typical Enterprise Capabilities artefacts used?
- Which challenges are being addressed by current Enterprise Capabilities artefacts
- What challenges are not being addressed by current models?
- Are there any underlying relationships between the Enterprise Capabilities artefacts
- Capability Architecture considerations:
- Typical Capabilities views in enterprise architecture, this includes:
- Business Architecture capability views
- Information Architecture capability views
- Technology Architecture capability views
- Typical Enterprise Capabilities Layered Architecture views
- Typical Capabilities views in enterprise architecture, this includes:
- Enterprise Capabilities LifeCycle considerations:
- Could Enterprise Capabilities be considered with a LifeCycle perspective?
- What would typical Enterprise Capabilities LifeCycle phases be?
- What would the Enterprise Capabilities LifeCycle tasks/steps be within the phases?
- Which Roles would typically be involved in the Enterprise Capabilities lifecycle?
- Could there be a Continuous feedback loop build into the Enterprise Capabilities LifeCycle?
- Enterprise Capabilities Maturity considerations:
- Does a maturity concept fit to Enterprise Capabilities?
- What are the most common maturity areas that could fit to Enterprise Capabilities?
- Categorization considerations:
- What are the most common categorization and classification used in Enterprise Capabilities concepts?
- Are there specific Categorization schemes?
- Are there specific Enterprise Capabilities concept tagging types
- Patterns
- What works well around Capability Modelling (repeatable patters)
Research Approach
When involving in such a complex industry research and analysis as defined in the research focus, this is where the Global University Alliance (GUA) has developed a unique collaborative process between academia and industry. As illustrated in figure 1, they do this through defining clear research themes, with detailed research questions, where they analyse and study patterns, describe capability concepts with their findings. This again can lead to additional research questions/themes as well as development of artefacts which can be used as reference content by practitioners and industry as a whole.
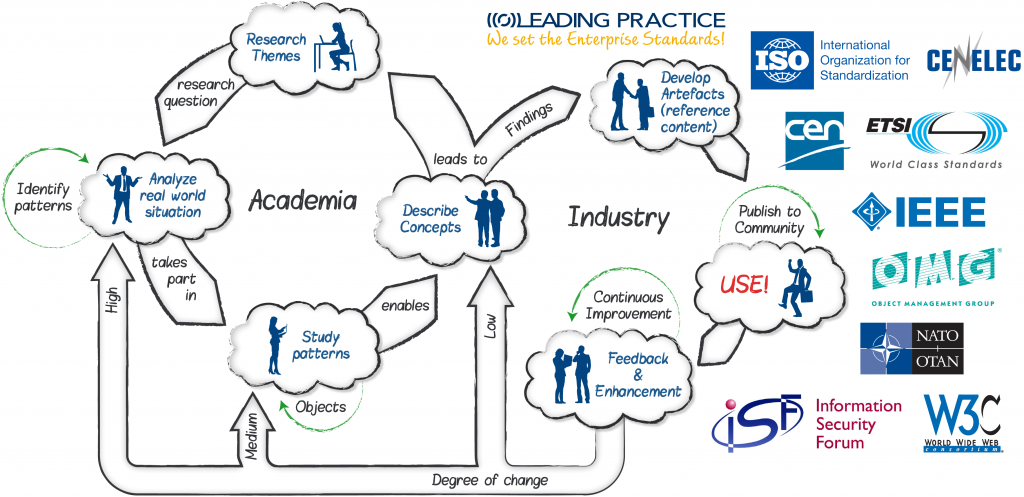
The Academia – Industry process has two types of different cycles. The one where Academia is leading the research and innovation, this is called the Academia Industry Research (AIR) process. The other is where practitioners from Industry describe concepts and develop artefacts and thereby they bring about innovation. This process is called the Academia Industry Design (AID). In order to establish both rigor as well as relevance, both of these loops are important for the Enterprise Capability research focus.
Research Findings
Examples of research findings can be found here:
- Capability Modelling:
- Capability Engineering
- Capability Architecture Development
- Relationship between Capability Engineering, Modelling & Architecture
- Capability and Artefacts
Enterprise Capabilities: What are they? (Part 1)
How to do Capability Modelling (Part 2)
Research Team
The Enterprise Capabilities research team and contacts are:
Research Leader:
Prof. Mark von Rosing
ISO 42010 Development Member
Global University Alliance, Chairman
OMG Business Architecture Special Interest Group, Co-Chair
OMG Academia & Research Working Group, Chair
The team involved in this work are among others the following academics, industry researchers and capability thought leaders:
- Enterprise Capability Ontology (meta objects), Prof. Wim Laurier (academic researcher)
- Enterprise Capability Semantics (relations and rules), Prof. Simon Polovina (academic researcher)
- Typical Capability Modelling concepts, Prof. Hans Scheruhn (academic researcher)
- Most common Enterprise Capability strategies applied, Jamie Caine (academic researcher)
- Most common Enterprise Capability KPIs, Ulrik Foldager (industry researcher)
- Most common Enterprise Capability Roles, Prof. Maxim Arzumanyan (academic researcher)
- Most common Enterprise Capability Stakeholder & Concerns, Maria Hove (industry researcher)
As far as partners are involved, these are the collaboration partner contacts:
Enterprise Standard Body:
Georg Etzel
LEADing Practice, Co-CEO
Enterprise Architecture Framework:
John A. Zachman
Inventor and Father of Enterprise Architecture
Zachman International
International Organization for Standardization
Johan H Bendz
ISO SC7
WG 42 Convener
IEEE Coordinator:
Rich Hilliard
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
Editor of IEEE Std 1471:2000, Project editor, ISO/IEC/IEEE 42010
Software Standards Body:
Henk De Man
OMG VDML Chairman
NATO Coordinators:
Johan Goossens
NATO Allied Command Transformation
Branch Head, Technology & Human Factors
UNESCO Coordinator:
Dr. Selin N. Şenocak
UNESCO Chair Holder
Cultural Diplomacy, Governance and Education
Director, Occidental Studies Applied Research Center
Political Sciences and International Relations Faculty Member
CSIR Coordinator:
Rentia Barnard
Research Institute CSIR
Enterprise Architect Research Group Leader
Information Security Standards Body:
Steve Durbin
CEO of Information Security Forum
OMG, Software Standards Body:
Fred Cummins
Business Modeling & Integration Task Force, Chairman
OMG Business Architecture Special Interest Group, Co-Chair
